[국내외기술동향] 포항공대 원자수준 뾰족한 양자광학용 나노안테나 개발, 나노공학의 혁신 예고 Development of Nan…
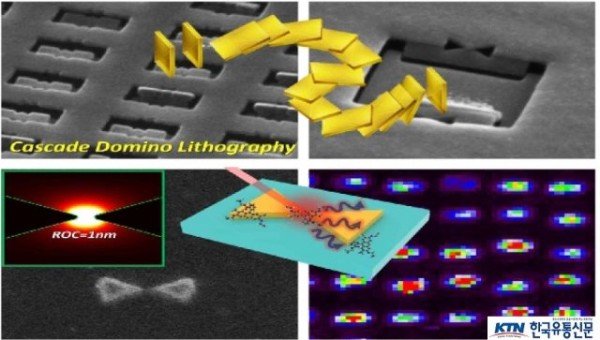
나노안테나와 이를 통해 구현된 초고민감도 나노센서(출처 이슈 포커스)
구미지역경제 이슈포커스(1)-원자수준의 양자광학용 나노안테나 개발
극한 광 집속 안테나
반도체 및 파운드리 산업 분야 단일 나노미터 수준의 해상도를 갖는 나노리소그래픽 기술
양자 정보 기술을 위한 고효율 단일 광자 소스 등 신 나노공학기술 분야 개척
(전국= KTN) 김도형 기자= 구미지역경제 이슈포커스에 소개된 내용에 따르면 원자수준의 뾰족한 양자 광학용 나노안테나 개발로 나노공학분야에 혁신을 이끌 것으로 예상된다.
이슈포커스에서는 국내 연구진이 수 나노미터 수준에서 일어나는 양자광학 현상에 대한 관찰이 가능한 초고밀도로 빛을 모으는 나노광학 안테나 개발에 성공했다고 하며 이는 원자수준으로 뾰족한(곡률반경 1mm) 극한 고아 집속 안테나다.
과학기술정보정보통신부는 포항공과대학교 노준석 교수팀이 원자수준 해상도의 나노 안테나 및 이를 제작하기 위한 나노공정 기술을 개발했다고 밝혔다.
이는 현존하는 나노공정 기술의 한계를 극복하는 연구성과로써 극한 나노광학 및 나노생산 기술에 기여할 수 있다는 가능성을 인정받아 세계적인 재료공학 분야 학술지인 머티리얼즈 투데이(Materials Today, IF=26.416)에 9월 2일 표지 논문으로게제됐다. 더불어 이 기술은 나노생산 분야 학술지 마이크로 시스템즈&나노엔지니어링(Microsystems and Nanoengineering, IF=5.616)에 9월 21일 게제됐다.
새로운 광학 현상을 탐구하기 위해서는 10nm 미만의 크기의 구조를 정교하게 제작하고 배열하는 기술이 필수적이기 때문에 많은 연구자들이 다양한 비전통적 나노가공 기술을 개발하고 있지만, 전자와 이온의 물리적인 회절 문제(전자와 이온이 모두 전하를 가지고 있어 강한 전압을 통해 빔을 접속해도 전자 또는 이온간 상호작용으로 인해 접속 가능한 빔의 크기가 제한됨)로 인해, 10nm 이하의 나노구조를 정교하고 날카롭게 제작.가공하는 것은 극히 어려운 난제로 여겨지고 있다.
이는 일반 기계가공에서 공구의 크기가 제작물의 크기를 제한하는 이유와 동일하다.
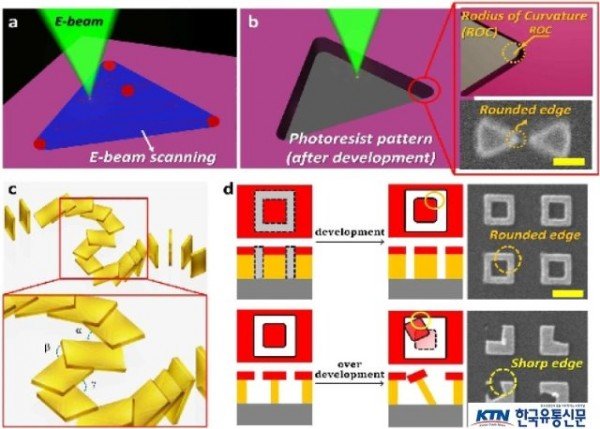
연구진은 이러한 난제를 해결하기 위해 도미노 놀이에서 영감을 얻어 새로운 방식의 연속 도미노 리소그래피 기술을 개발했고, 이를 통해 기존 전자빔 리소그래피에서 제약받는 해상도를 원자수준으로 뾰족하게 만들어 나비넥타이 형태의 나노안테나를 개발하는데 성공했다.
일반적인 나노구조 제작에 사용되는 전자빔 리소그래피 기술을 기반으로, 도미노에서 일어나는 구조의 쓰러짐 현상을 포토레지스트 구조에 의도적으로 접목시켜, 쓰러진 구조의 선과 선이 만나는 곳의 이상적인 뾰족한 부분을 활용해 1mm 이하의 곡률을 갖는 뾰족한 나노구조를 제작한 것이다.
이 나노안테나는 1nm이하의 곡률을 갖는 것과 동시에 5nm 정도의 나노갭 공간을 갖고 있으며, 이 미세 공간상의 빛는 5만 배 이상의 세기를 가지며 태양표면 에너지 밀도의 100만배에 해당되는 극한으로 집속된다.
이렇게 강하게 집속되는 빛을 바탕으로 단분자 수준을 검출할 수 있는 초고민감도 바이오센서를 실험적으로 구현했다. 또한 현재는 양자광학적 특성인 양자 플라즈모닉스 및 강한 결합 현상 등을 관찰할 수 있는 극한 나노 및 양자광학 플랫폼을 마련하여 후속 연구를 진행 중이다.
*양자플라즈모닉스: 파장보다 극히 작은 영역에서 집속되는 빛을 플라즈모닉스라고 하고, 이의 양자역학적 특성을 관찰하는 분야를 양자 플라즈모닉스라고 일컷는다.
*강한결합: 빛이 강하게 집속되는 나노공진기와 빛을 내뿜는 방사체가 서로 강한 결합이 되어있는 상황을 나타내는 물리적 특성이다.
극한 광 집속 나노안테나는 이러한 극한 나노광학 연구뿐만 아니라, 현재 반도체 및 파운드리 산업에서 가장 중요한 이슈 가운데 하나인 단일 나노미터 수준의 해상도를 갖는 나노리소그래픽 기술, 그리고 양자 정보 기술을 위한 고효율 단일 광자 소스 등과 같은 새로운 나노공학 분야를 개척할 수 있을 것으로 기대하고 있다.
본 연구성과는 과학기술정보통신부 글로벌프런티어사업, 중견연구자지원사업, RLRC사업, ERC사업, 미래소재디스커버리사업, 글로벌박사펠로우십 등의 지원을 받아 수행했다.
기존 전자빔 리소그래피 공정의 한계(출처 이슈 포커스)
Development of Nano-anthena for Quantum Optics at the Atomic Level of Pohang University of Science and Technology and Prediction of Innovation in Nanotechnology
Gumi Regional Economic Issue Focus (1)-Development of Quantum Optics Nanothena at Atomic Level
Extreme Optical Concentration Antenna
Nanosographic technology with single nanometer-level resolution in semiconductor and foundry industries
Exploring new nanotechnology fields such as high-efficiency single photon sources for quantum information technology
(National = KTN) Reporter Kim Do-hyung: According to an introduction in the Gumi Regional Economic Issues Focus published by the Gumi Electronics Information Technology Institute, it is expected that the development of nano-antics for pointed quantum optics at the atomic level will lead to innovation in nanotechnology.
In Issue Focus, Korean researchers have successfully developed nanoptical antennas that collect light at ultra-dense levels that allow observation of quantum optics occurring at several nanometers levels, which are pointed at atomic levels (1mm in radius of curvature) extreme orphaned antennas.
The Ministry of Science, Technology, Information and Communication announced that a team led by Professor Noh Joon-seok of Pohang University of Science and Technology has developed nano antennas with atomic-level resolution and nanotechnology to produce them.
This was published on September 2 in the journal Materials Today (IF=26.416), a world-renowned journal of materials engineering, in recognition of its potential to contribute to extreme nanoparticles and nanoproduction technologies as research achievements that overcome the limitations of existing nanoprocessing technologies. In addition, this technology was published on September 21 in MicroSystems and Nano Engineering (IF=5.616), an academic journal in the field of nano-production.
To explore new optical phenomena, many researchers are developing a variety of non-traditional nano-processing technologies because the technology to fine-tune and arrange structures of less than 10 nm is essential, but due to physical diffraction problems of electrons and ions (both electrons and ions have electric charges, so connecting beams through strong voltages limits the size of accessible beams due to electronic or ion-to interaction), the nanostructures less than 10 nm are sophisticated and sharp.Processing is considered an extremely difficult challenge.
This is the same reason why the size of the tool in general machining limits the size of the workpiece.
To solve these challenges, the researchers took inspiration from domino play and developed a new method of continuous domino lithography, which succeeded in developing a bow tie-shaped nano-antenna by making the resolution constrained by existing electron beam lithography pointed to atomic level.
Based on the electron beam lithography technology used in general nanostructures, the collapse of the structure occurring in dominoes is intentionally incorporated into the photoresist structure, and a pointed nanostructure with a curvature of less than 1mm is produced by utilizing the ideal sharp spot where the lines of the fallen structure meet.
The nanothena has a curvature of less than 1 nm and has a nano-gap space of about 5 nm, and the light in this microspace has more than 50,000 times the intensity and is concentrated at an extreme level equal to 1 million times the energy density of the solar surface.
Based on light that is strongly concentrated, ultra-sensitivity bio-sensors that can detect monomolecular levels are experimentally. In addition, we are currently conducting follow-up research by preparing an extreme nano and quantum optical platform that can observe quantum optical properties such as quantum Plasmonyx and strong binding phenomena.
* Quantum Plasmonyx: Light that is concentrated in areas that are very small than wavelengths is called Plasmonyx, and the field that observes its quantum mechanical properties is called quantum Plasmonyx.
*Strong bond: A physical characteristic of a situation in which the light is strongly concentrated and the emitting emitters are strongly bound together.
Extreme light-concentrated nanothena is expected to explore not only these extreme nanoprotechnical studies, but also new nanotechnology fields such as nanoscophic technology with single nanometer-level resolution, one of the most important issues in the semiconductor and foundry industry today, and high-efficiency single photon sources for quantum information technology.
This research result was carried out with support from the Global Frontier Project of the Ministry of Science and ICT, Mid-sized Research Support Project, RLRC Project, ERC Project, Future Materials Discovery Project, and Global Doctor Fellowship.
<저작권자(c)한국유통신문. 무단전재-재배포 금지>
기사제보 및 사회적 공헌활동 홍보기사 문의: 010-3546-9865, flower_im@naver.com
해썹문의: 010-3546-9865
제품광고: 코로나19 극복 면역력 강화 새싹보리 튼튼건강환(기업체 사은품 대량 주문 문의 01035469865)
[국내외기술동향] 원자수준으로 뾰족한 양자광학용 나노안테나 개발, 나노공학의 혁신 예고
Comments